Understanding USDA plant zones is crucial even if you reside in Florida, famous for its warm and sunny climate.
Although subset plant zones have the letter A in it, Zone A Florida signifies evacuation zones instead of plant hardiness.
Thus, stick with the article till the end to understand Florida plant zones and best gardening tips.
Understanding USDA Zones in Florida
There are 13 growing, or gardening zones subdivided based on the average lowest temperatures.
As the USDA zone tells you the estimated lowest temperature for the area, you can preplan what and when to plant.
The state’s overall climate is subtropical and humid as the Florida plant zones start from 8a.
Cities in the south and central of Florida have higher plant zones like 9 and 10.
Meanwhile, areas that are far north of Florida mainly lie within plant zone 8, and if you are in the southern Florida Keys, it is the 11a hardiness zone.
- Zones 8a and 8b (10-20°F): Covers cities like Tallahassee, Panhandle, Destin and most parts of Panama.
- Zones 9a and 9b (20-30°F): Includes Gainesville, Ocala, Orlando, Kissimmee, Titusville and Tampa, like major cities.
- Zones 10a and 10b (30-40°F): Clearwater, Naples and Fort Myers fall under planting zone 10.
- Zones 11a (40-45°F): The southernmost tip of the Florida Keys is the area with the 11a USDA gardening zone.
If you are having trouble finding the USDA zone on the map, use your Zip code to find planting zones on the website of USDA.
Do you know over three-quarters of midwinter Strawberries are produced in Plant City, Florida, which lies in the 9b USDA planting zone?
Best Tips to Grow Plants in Florida USDA Zones
With prior knowledge of USDA zones, you can plant crops in a planned fashion and keep your gardening thriving all year round.
Thus, carefully curate a plant list that can thrive in the climatic conditions of the hardiness zones of Florida.
- The surrounding terrains can alter the climate despite being in the same planting zone, meaning it can get a bit hotter or cooler. So, carefully adjust the plant care routine.
- As summer is cruel in Florida, keep outdoor plants in the shade of tall trees.
- Keep up with the summer heat and water your plants regularly to keep them hydrated.
- Winter garden vegetables like Kale, Lettuce, Carrots, etc., can tolerate the winter of northern Florida.
- After the final frost date, you can start planting veggies outdoors.
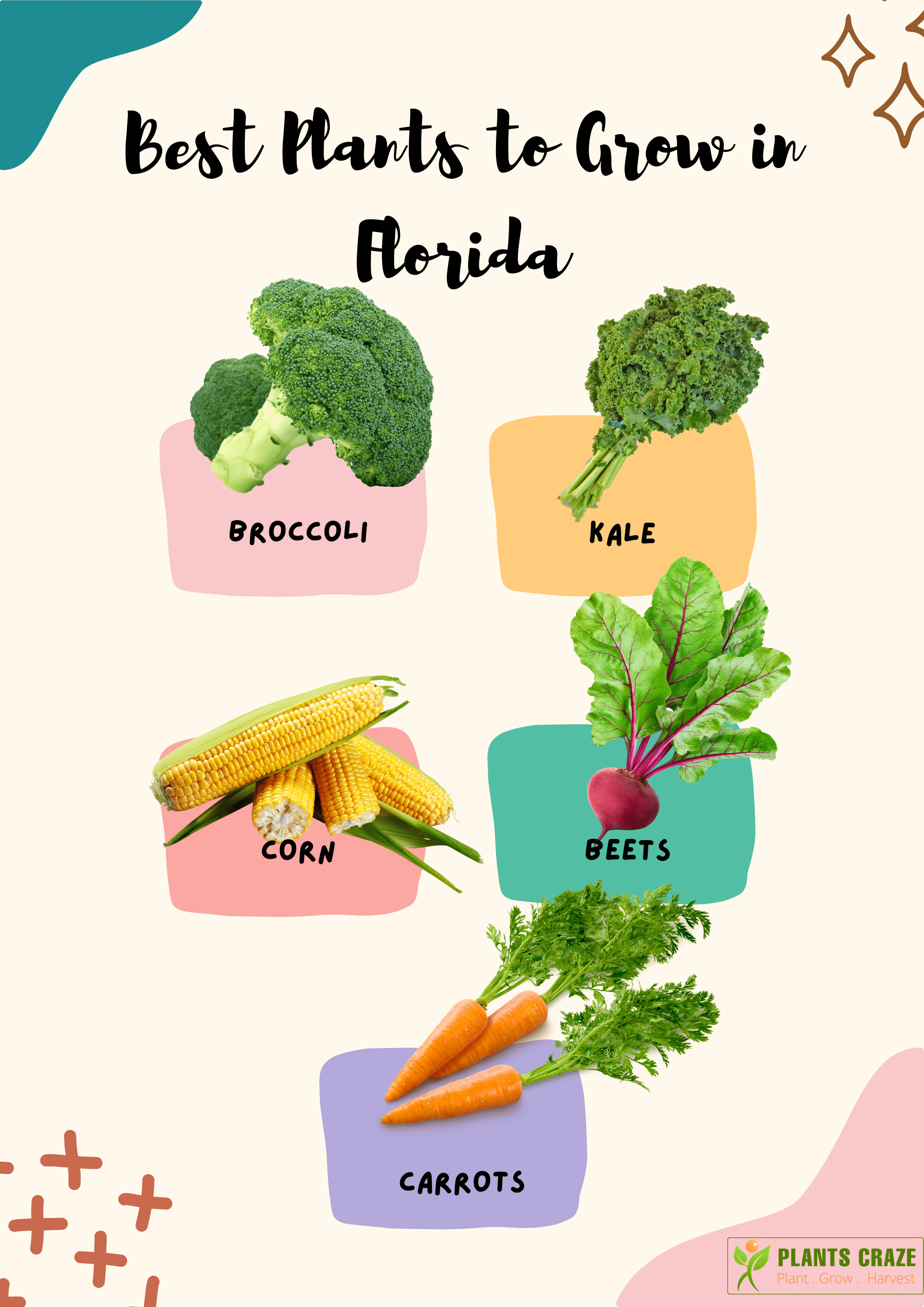
- Grow vegetables like Broccoli, Cabbage, Collards, Corn and Beets, as they are the best vegetables to grow in Florida.
- Add Blue Daze, Lantana, Lavender, Pentas, Blue Salvia Petunia, Sunflower, etc., to add a little splash of color to your garden.
Editor’s Note
Florida: Long Brutal Summer But Mild Winter!
The cruel summer of Florida can quickly dehydrate plants in summer, so consistently adjust and water your garden in the morning.
Also, use organic mulching, which can prolong the soil’s moisture retention in summer and can help trap heat during frost nights.
All The Best!
